Overview
There does not exist a unified benchmark such as GLUE in hate speech detection domain that conducts a leaderboard style performance comparison of different open-source hate speech classifiers. This prevents the practitioners from making informed decisions when choosing which model to use for their own hate speech detection applications.
The benchmark will provide the following:
- The entire training and validation set for future study. However, the labels from public test sets will not be released for benchmarking purposes; there will be additional private test sets.
- The ranking of the models based on the average aggregated metrics (for example, F1 score) on the public and private test sets.
Protocol
Candidate Datasets
Collected Datasets from Diverse Topics
The current data aggregation includes [1] through [5], where the [5] only includes hate speech.
- Detecting East Asian Prejudice on Social Media (Vidgen et al., ALW 2020)
- [2005.12423] Racism is a Virus: Anti-Asian Hate and Counterspeech in Social Media during the COVID-19 Crisis (He et al.)
- [2108.12521] TweetBLM: A Hate Speech Dataset and Analysis of Black Lives Matter-related Microblogs on Twitter (Kumar et al.)
- Hate Towards the Political Opponent: A Twitter Corpus Study of the 2020 US Elections on the Basis of Offensive Speech and Stance Detection (Grimminger & Klinger, WASSA 2021)
- Latent Hatred: A Benchmark for Understanding Implicit Hate Speech (ElSherief et al., EMNLP 2021)
cardiffnlp/twitter-roberta-base-hate-latest Collection
The follow are the datasets used for the model cardiffnlp/twitter-roberta-base-hate-latest or the paper below:
Robust Hate Speech Detection in Social Media: A Cross-Dataset Empirical Evaluation (Antypas & Camacho-Collados, WOAH 2023)
The following are the papers that correspond to the list of datasets:
- SemEval-2019 Task 5: Multilingual Detection of Hate Speech Against Immigrants and Women in Twitter (Basile et al., SemEval 2019)
- The Measuring Hate Speech Corpus: Leveraging Rasch Measurement Theory for Data Perspectivism (Sachdeva et al., NLPerspectives 2022)
- Detecting East Asian Prejudice on Social Media (Vidgen et al., ALW 2020)
- [2004.12764] “Call me sexist, but…”: Revisiting Sexism Detection Using Psychological Scales and Adversarial Samples (Samory et al.)
- Predicting the Type and Target of Offensive Posts in Social Media (Zampieri et al., NAACL 2019)
- [2012.10289] HateXplain: A Benchmark Dataset for Explainable Hate Speech Detection (Mathew et al.)
- [1802.00393] Large Scale Crowdsourcing and Characterization of Twitter Abusive Behavior (Founta et al.)
- Multilingual and Multi-Aspect Hate Speech Analysis (Ousidhoum et al., EMNLP-IJCNLP 2019)
- [2108.05927] Overview of the HASOC track at FIRE 2020: Hate Speech and Offensive Content Identification in Indo-European Languages (Mandal et al.)
- Are You a Racist or Am I Seeing Things? Annotator Influence on Hate Speech Detection on Twitter (Waseem, NLP+CSS 2016)
- [1703.04009] Automated Hate Speech Detection and the Problem of Offensive Language (Davidson et al.)
- Hate Towards the Political Opponent: A Twitter Corpus Study of the 2020 US Elections on the Basis of Offensive Speech and Stance Detection (Grimminger & Klinger, WASSA 2021)
- Hateful Symbols or Hateful People? Predictive Features for Hate Speech Detection on Twitter (Waseem & Hovy, NAACL 2016)
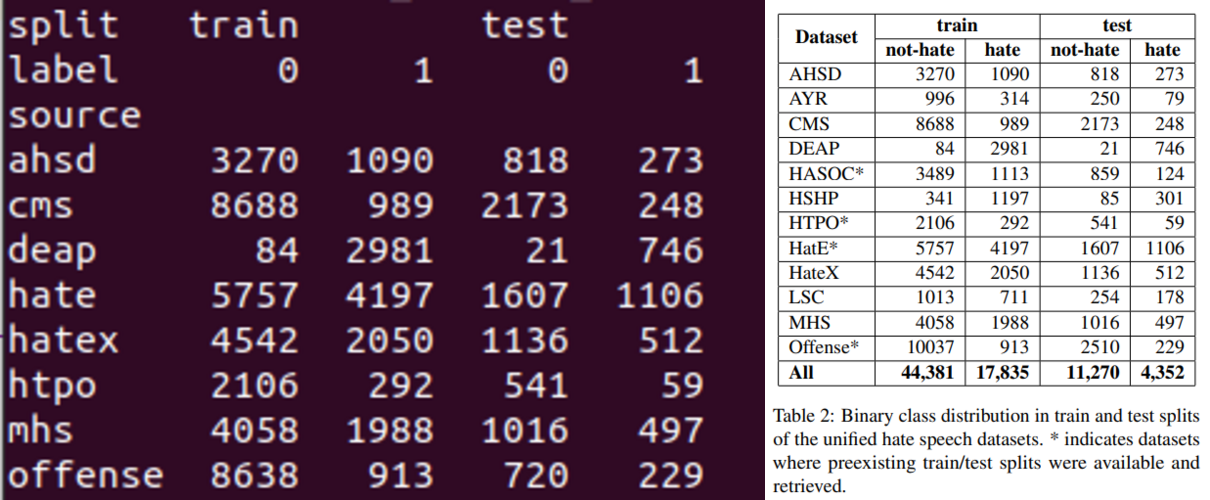
It is possible to approximate a subset of the original training mixture (8 of 12 datasets excluding the MMHS dataset, which only includes hate speech) following the Table 2 of the original paper. Something to note is that:
- AYR, HASOC, HSHP, and LSC are not usable.
- Offense does not exactly match the sizes in Table 2.
- We disregard any splits and try to match the number in Table 2. When matching number is not possible, we try to make sure the ratio of
on-hate versus hate is same.
Additional Datasets from hatespeechdata.com
The following the the additional datasets from hatespeechdata.com that are not included in the above mentioned sources. The dataset names are either available from the original paper or created here for easy reference.
| Index |
Dataset Name |
Source |
Notes |
| 1 |
AbuseEval |
GitHub |
The Offense dataset above reannotated for non-hate, implicit, and explicit hate; only IDs are available. Around 87% of the hate/non-hate labels are same as the previous Offense dataset. |
| 2 |
SWAD |
GitHub |
|
| 3 |
ALONE |
|
Not usable. Requires contacting authors. |
| 4 |
HatefulUsersTwitter |
GitHub and Kaggle |
Available but not relevant. This dataset is about detecting whether a user is hateful or neutral on the Tweet network; it does not come with annotated hateful/benign texts. |
| 5 |
MMHS150K |
Website |
Not usable. Multimodal datasets. |
| 6 |
HarassmentLexicon |
GitHub |
Not usable. Lexicons only. |
| 7 |
P2PHate |
GitHub |
Not usable. Dehydrated. |
| 8 |
Golbeck |
|
Not usable. Requires contacting jgolbeck@umd.edu |
| 9 |
SurgeAI |
Website |
Hateful content only. |
| 10 |
TSA |
Kaggle |
Dataset is provided by Analytics Vidhya. The test.csv does not come with labels. |
- I Feel Offended, Don’t Be Abusive! Implicit/Explicit Messages in Offensive and Abusive Language (Caselli et al., LREC 2020): The dataset from this paper is also called AbuseEval v1.0.
- Do You Really Want to Hurt Me? Predicting Abusive Swearing in Social Media (Pamungkas et al., LREC 2020)
- [2008.06465] ALONE: A Dataset for Toxic Behavior among Adolescents on Twitter (Wijesiriwardene et. al.)
- [1803.08977] Characterizing and Detecting Hateful Users on Twitter (Ribeiro et al., ICWSM 2018)
- [1910.03814] Exploring Hate Speech Detection in Multimodal Publications (Gomez et al., WACV 2020)
- [1802.09416] A Quality Type-aware Annotated Corpus and Lexicon for Harassment Research (Rezvan et al.)
- [1804.04649] Peer to Peer Hate: Hate Speech Instigators and Their Targets (ElSherief et al.)
- A Large Labeled Corpus for Online Harassment Research (Golbeck et al., WebSci 2017)
- Twitter Hate Speech Dataset (Surge AI)
- Twitter Sentiment Analysis (Kaggle)
