[YouTube] – [Personal Website]
- The presenter has authored several interesting papers ([1] through [5]) on hate speech detection.
Contents
Notes
Status Quo of Hate Speech Detection
- There are varying definitions of hate speech.
- Labels related to hate speech include hate, offensive, toxic, profane, and toxic. There could be also more fine-grained categories, such as sexist, racist, and islamophobic.
- Because of the reasons mentioned above, there is no leaderboard in hate speech detection.
Data Sources
We should pay attention to data bias; it is doubtful to collect hate speeches from people and sites that are more likely to generate hate speech. The authors propose to collect datasets from neutral sources; this design choice makes the data annotation difficult.
Annotations
Current approaches of hate speech annotation rely on people (crowdworkers or experts). The authors use the two-phase approach to ensure the label quality.
Building Better Hate Speech Detection Models
- The complexity of models does not necessarily help. It is more important to capture the signals that predict the final labels, for example, the history and the social network information. This observation also applies to other tasks that involve modeling social behaviors.
- However, we should carefully monitor the overfitting: spurious correlation between overfitted phrases and labels should not be the signals we allow the models to pick up. That is, the models should generalize without the presence of these words.
- In the work [2], the authors propose a system that considers not just the text information, but also the timeline and social network information. They merge the three sources of signal using an attention mechanism. However, we could see two limitations:
- This design is specific to Twitter. Other platforms, such as Reddit, do not have this information with respect to users.
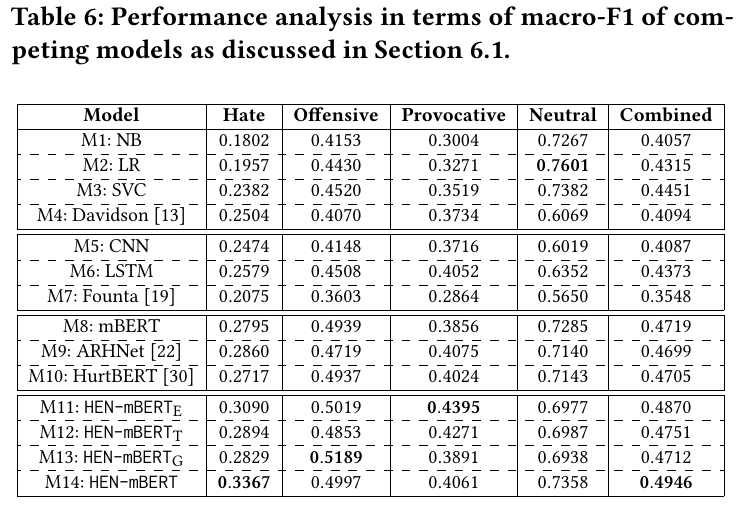
- The best performing system (
M14) does not significantly outperform the baseline system, which is simply fine-tuning a mBERT (M8).
Lexical Bias
- Replacing the bias sensitive words with more general words is likely shift the bias towards the WordNet ancestors. This hypothesis could be supported by a measurement called pinned bias, where t is the single word in the sensitive word list.
pB _ T = \sum _ {t \in T} \frac{\vert p(\text{“toxic”}\vert t) – \phi\vert}{ \vert T \vert},\quad \phi=\min(p(\text{“toxic”}\vert t), 0.5)
Horizons
The presenter has three high-level observations:
- Like energy: Bias seems to be transferring from one source to the other.
- Like a system at rest: A model or dataset will remain biased unless external force (for example, mitigation and regularization) is enabled.
- Like interactive systems: A system is evolving more chaotic over time. The toxicity needs to be monitored and mitigated in a continuous fashion.
Reference
- [2010.04377] Hate is the New Infodemic: A Topic-aware Modeling of Hate Speech Diffusion on Twitter (Masud et al., ICDE 2021): This paper presents a dataset called RETINA that focus on hate speech in the Indian context.
- [2206.04007] Proactively Reducing the Hate Intensity of Online Posts via Hate Speech Normalization (Masud et al., KDD 2022)
- [2201.00961] Nipping in the Bud: Detection, Diffusion and Mitigation of Hate Speech on Social Media (Chakraborty and Masud)
- [2306.01105] Revisiting Hate Speech Benchmarks: From Data Curation to System Deployment (Masud et al., KDD 2023)
- [2202.00126] Handling Bias in Toxic Speech Detection: A Survey (Garg et al., CSUR).
- Language (Technology) is Power: A Critical Survey of “Bias” in NLP (Blodgett et al., ACL 2020)
- [2305.06626] When the Majority is Wrong: Modeling Annotator Disagreement for Subjective Tasks (Fleisig et al.)
- Handling Disagreement in Hate Speech Modelling | SpringerLink (Novak et al., IPMU 2022)
- [2001.05495] Stereotypical Bias Removal for Hate Speech Detection Task using Knowledge-based Generalizations (Badjatiya et al., WWW 2019).